History

An evolution of mobile phones
Radiophones have a long and varied history going back to
Reginald Fessenden's invention and shore-to-ship demonstration of radio telephony, through the
Second World War with military use of radio telephony links and civil services in the 1950s.
The first mobile telephone call made from a car occurred in
St. Louis, Missouri, USA on June 17, 1946, using the
Bell System's
Mobile Telephone Service. The equipment weighed 80 pounds (36 kg), and the
AT&T service, basically a massive party line, cost US$30 per month (equal to $337.33 today) plus 30–40 cents per local call, equal to $3.37 to $4.5 today.
[5]In 1956, the world’s first partly
automatic car phone system, Mobile System A (MTA), was launched in Sweden. MTA phones were composed of
vacuum tubes and
relays, and had a weight of 40 kg. In 1962, a more modern version called
Mobile System B (MTB) was launched, which was a
push-button telephone, and which used
transistors to enhance the telephone’s calling capacity and improve its operational reliability, thereby reducing the weight of the apparatus to 10 kg. In 1971, the
MTD version was launched, opening for several different brands of equipment and gaining commercial success.
[6][7]Martin Cooper, a
Motorola researcher and executive is considered to be the inventor of the first practical mobile phone for
handheld use in a non-vehicle setting, after a long race against
Bell Labs for the first portable mobile phone. Using a modern, if somewhat heavy portable handset, Cooper made the first call on a handheld mobile phone on April 3, 1973 to his rival, Dr.
Joel S. Engel of
Bell Labs.
[8] The first commercially automated cellular network (the
1G) was launched in Japan by
NTT in 1979, initially in the metropolitan area of Tokyo. Within five years, the NTT network had been expanded to cover the whole population of Japan and became the first nationwide 1G network. In 1981, this was followed by the simultaneous launch of the
Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) system in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden.
[9] NMT was the first mobile phone network featuring international
roaming. The first 1G network launched in the USA was Chicago-based
Ameritech in 1983 using the
Motorola DynaTAC mobile phone. Several countries then followed in the early-to-mid 1980s including the UK, Mexico and Canada.
The first "modern" network technology on digital
2G (second generation) cellular technology was launched by
Radiolinja (now part of
Elisa Group) in 1991 in Finland on the
GSM standard, which also marked the introduction of competition in mobile telecoms when Radiolinja challenged incumbent
Telecom Finland(now part of
TeliaSonera) who ran a 1G NMT network.
Before cellular networks

A mobile radio telephone.
Mobile radio telephone systems preceded modern cellular mobile telephony technology. Since they were the predecessors of the first generation of cellular telephones, these systems are sometimes retroactively referred to as
pre cellular (or sometimes zero generation) systems. Technologies used in pre cellular systems included the
Push to Talk (PTT or manual),
Mobile Telephone System (MTS),
Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS), and
Advanced Mobile Telephone System (AMTS) systems. These early mobile telephone systems can be distinguished from earlier closed
radiotelephone systems in that they were available as a commercial service that was part of the
public switched telephone network, with their own telephone numbers, rather than part of a closed network such as a police radio or taxi dispatch system.
These mobile telephones were usually mounted in cars or trucks, though briefcase models were also made. Typically, the transceiver (transmitter-receiver) was mounted in the vehicle trunk and attached to the "head" (dial, display, and handset) mounted near the driver seat.
They were sold through WCCs (Wireline Common Carriers, AKA telephone companies), RCCs (Radio Common Carriers), and two-way radio dealers.
Origins
Early examples for this technology:
- Motorola in conjunction with the Bell System operated the first commercial mobile telephone service Mobile Telephone System (MTS) in the US in 1946, as a service of the wireline telephone company.
- The A-Netz launched 1952 in West Germany as the country's first public commercial mobile phone network.
- First automatic system was the Bell System's IMTS which became available in 1962, offering automatic dialing to and from the mobile.
- The Televerket opened its first manual mobile telephone system in Norway in 1966. Norway was later the first country in Europe to get an automatic mobile telephone system.
- The Autoradiopuhelin (ARP) launched in 1971 in Finland as the country's first public commercial mobile phone network
- The B-Netz launched 1972 in West Germany as the country's second public commercial mobile phone network (but the first one that did not require human operators to connect calls)
Radio Common Carrier
Parallel to
Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS) in the US until the rollout of cellular AMPS systems, a competing mobile telephone technology was called
Radio Common Carrier or
RCC. The service was provided from the 1960s until the 1980s when cellular AMPS systems made RCC equipment obsolete. These systems operated in a regulated environment in competition with the Bell System's MTS and IMTS. RCCs handled telephone calls and were operated by private companies and individuals. Some systems were designed to allow customers of adjacent RCCs to use their facilities but the universe of RCCs did not comply with any single interoperable technical standard (a capability called
roaming in modern systems). For example, the phone of an Omaha, Nebraska–based RCC service would not be likely to work in Phoenix, Arizona. At the end of RCC's existence, industry associations were working on a technical standard that would potentially have allowed roaming, and some mobile users had multiple decoders to enable operation with more than one of the common signaling formats (600/1500, 2805, and Reach). Manual operation was often a fallback for RCC roamers.
Roaming was not encouraged, in part, because there was no centralized industry billing database for RCCs. Signaling formats were not standardized. For example, some systems used
two-tone sequential paging to alert a mobile or hand-held that a wired phone was trying to call them. Other systems used
DTMF. Some used a system called
Secode 2805 which transmitted an interrupted 2805 Hz tone (in a manner similar to IMTS signaling) to alert mobiles of an offered call. Some radio equipment used with RCC systems was half-duplex, push-to-talk equipment such as Motorola hand-helds or RCA 700-series conventional two-way radios. Other vehicular equipment had telephone handsets, rotary or pushbutton dials, and operated full duplex like a conventional wired telephone. A few users had full-duplex briefcase telephones (radically advanced for their day).
RCCs used paired UHF 454/459 MHz and VHF 152/158 MHz frequencies near those used by IMTS.
Rural Radiotelephone Service
Systems used UHF 454 MHz or 152 MHz radio channels to provide telephone service to extremely rural places where it would be too costly to extend cable plant. One such system was on a 454/459 MHz channel pair between the
Death Valley telephone exchange and
Stovepipe Wells, California. This specific system carried manual calls to the Traffic Service Position System (TSPS) center in Los Angeles. Stovepipe Wells callers went off-hook and were queried, "Number please," by a TSPS operator, who dialed the call. Dial service was introduced to Stovepipe Wells in the mid-1980s. The radio link has since been replaced by cable. The analog service has since been replaced by
Basic Exchange Telephone Radio Service, a digital system using the same frequencies.
Features
All mobile phones have a number of features in common, but manufacturers also try to differentiate their own products by implementing additional functions to make them more attractive to consumers. This has led to great innovation in mobile phone development over the past 20 years.
The common components found on all phones are:
- A battery, providing the power source for the phone functions
- An input mechanism to allow the user to interact with the phone. The most common input mechanism is a keypad, but touch screens are also found in some high-end smartphones.
- Basic mobile phone services to allow users to make calls and send text messages.
- All GSM phones use a SIM card to allow an account to be swapped among devices. Some CDMA devices also have a similar card called a R-UIM.
- Individual GSM, WCDMA, iDEN and some satellite phone devices are uniquely identified by an International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number.
Low-end mobile phones are often referred to as
feature phones, and offer basic telephony, as well as functions such as playing music and taking photos, and sometimes simple applications based on generic
managed platforms such as
Java ME or BREW. Handsets with more advanced computing ability through the use of native software applications became known as
smartphones. The first smartphone was the
Nokia 9000 Communicator in 1996 which added
PDA functionality to the basic mobile phone at the time. As miniaturization and increased processing power of microchips has enabled ever more features to be added to phones, the concept of the smartphone has evolved, and what was a high-end smartphone five years ago, is a standard phone today.
Several phone series have been introduced to address a given market segment, such as the RIM
BlackBerry focusing on enterprise/corporate customer email needs; the SonyEricsson Walkman series of musicphones and Cybershot series of cameraphones; the
Nokia Nseries of multimedia phones, the
Palm Pre the
HTC Dream and the Apple
iPhone.
Other features that may be found on mobile phones include
GPS navigation, music (MP3) and video (
MP4) playback,
RDS radio receiver, alarms, memo recording,
personal digital assistant functions, ability to watch
streaming video, video download,
video calling,
built-in cameras (1.0+
Mpx) and
camcorders (video recording), with
autofocus and flash,
ringtones, games,
PTT,
memory card reader(SD),
USB (2.0), dual line support,
infrared,
Bluetooth (2.0) and
WiFi connectivity,
instant messaging, Internet e-mail and
browsing and serving as a
wireless modem.
Nokia and the University of Cambridge demonstrated a
bendable cell phone called the
Morph.
[12] Some phones can make
mobile payments via direct mobile billing schemes or through
contactless payments if the phone and
point of sale support
Near Field Communication (NFC).
[13] Some of the largest mobile phone manufacturers and network providers along with many retail merchants support, or plan to support, contactless payments through NFC-equipped mobile phones.
[14][15][16]Some phones have an electromechanical
transducer on the back which changes the electrical voice signal into mechanical vibrations. The vibrations flow through the cheek bones or forehead allowing the user to hear the conversation. This is useful in the noisy situations or if the user is hard of hearing.
[17]Software and applications
The most commonly used data application on mobile phones is
SMS text messaging. The first SMS text message was sent from a computer to a mobile phone in 1992 in the UK, while the first person-to-person SMS from phone to phone was sent in Finland in 1993.
Other non-SMS data services used on mobile phones include mobile music, downloadable logos and pictures, gaming, gambling, adult entertainment and advertising. The first downloadable mobile content was sold to a mobile phone in Finland in 1998, when Radiolinja (now Elisa) introduced the downloadable ringtone service. In 1999, Japanese mobile operator NTT DoCoMo introduced its mobile Internet service,
i-Mode, which today is the world's largest mobile Internet service.
The first mobile news service, delivered via SMS, was launched in Finland in 2000.
Mobile news services are expanding with many organizations providing "on-demand" news services by SMS. Some also provide "instant" news pushed out by SMS.
Mobile payments were first trialled in Finland in 1998 when two Coca-Cola vending machines in Espoo were enabled to work with SMS payments. Eventually, the idea spread and in 1999 the Philippines launched the first commercial mobile payments systems, on the mobile operators Globe and Smart. Today, mobile payments ranging from
mobile banking to mobile credit cards to mobile commerce are very widely used in Asia and Africa, and in selected European markets.
Power supply

Mobile phone charging service in Uganda
Mobile phones generally obtain power from
rechargeable batteries. There are a variety of ways used to charge cell phones, including
USB, portable batteries, mains power (using an
AC adapter), cigarette lighters (using an adapter), or a
dynamo. In 2009, the first wireless charger was released for consumer use.
[18]Various initiatives, such as the EU
Common External Power Supply have been announced to standardize the interface to the charger, and to promote energy efficiency of mains-operated chargers. A star rating system is promoted by some manufacturers, where the most efficient chargers consume less than 0.03 watts and obtain a five-star rating.

The world's five largest handset makers introduced a new rating system in November 2008 to help consumers more easily identify the most energy-efficient chargers
Battery
Formerly, the most common form of mobile phone batteries were
nickel metal-hydride, as they have a low size and weight.
Lithium ion batteries are sometimes used, as they are lighter and do not have the
voltage depression that nickel metal-hydride batteries do. Many mobile phone manufacturers have now switched to using
lithium–polymer batteries as opposed to the older
Lithium-Ion, the main advantages of this being even lower weight and the possibility to make the battery a shape other than strict cuboid.
[20] Mobile phone manufacturers have been experimenting with alternative power sources, including
solar cells. A prototype mini solar panel from Wysips was able use perfectly as 'live phone' with Android phone. The mini solar panel can be installed on the Android phone screen, although the phone battery is still needed due to the solar panel solely has not been able to produce enough energy.
[21]SIM card
GSM mobile phones require a small
microchip called a Subscriber Identity Module or
SIM Card, to function. The SIM card is approximately the size of a small postage stamp and is usually placed underneath the battery in the rear of the unit. The SIM securely stores the
service-subscriber key (IMSI) used to identify a subscriber on mobile telephony devices (such as mobile phones and computers). The SIM card allows users to change phones by simply removing the SIM card from one mobile phone and inserting it into another mobile phone or broadband telephony device.
A SIM card contains its unique serial number, internationally unique number of the mobile user (
IMSI), security authentication and ciphering information, temporary information related to the local network, a list of the services the user has access to and two passwords (PIN for usual use and PUK for unlocking).
SIM cards are available in three standard sizes. The first is the size of a credit card (85.60 mm × 53.98 mm x 0.76 mm). The newer, most popular miniature version has the same thickness but a length of 25 mm and a width of 15 mm, and has one of its corners truncated (chamfered) to prevent misinsertion. The newest incarnation known as the 3FF or micro-SIM has dimensions of 15 mm × 12 mm. Most cards of the two smaller sizes are supplied as a full-sized card with the smaller card held in place by a few plastic links; it can easily be broken off to be used in a device that uses the smaller SIM.
The first SIM card was made in 1991 by Munich smart card maker
Giesecke & Devrient for the Finnish wireless network operator
Radiolinja. Giesecke & Devrient sold the first 300 SIM cards to Elisa (ex. Radiolinja).
Those cell phones that do not use a SIM Card have the data programmed in to their memory. This data is accessed by using a special digit sequence to access the "NAM" as in "Name" or number programming menu. From there, information can be added, including a new number for the phone, new Service Provider numbers, new emergency numbers, new Authentication Key or A-Key code, and a Preferred Roaming List or PRL. However, to prevent the phone being accidentally disabled or removed from the network, the Service Provider typically locks this data with a Master Subsidiary Lock (MSL). The MSL also
locks the device to a particular carrier when it is sold as a
loss leader.
The MSL applies only to the SIM, so once the contract has expired, the MSL still applies to the SIM. The phone, however, is also initially locked by the manufacturer into the Service Provider's MSL. This lock may be disabled so that the phone can use other Service Providers' SIM cards. Most phones purchased outside the U.S. are unlocked phones because there are numerous Service Providers that are close to one another or have overlapping coverage. The cost to unlock a phone varies but is usually very cheap and is sometimes provided by independent phone vendors.
Multi-card hybrid phones
A hybrid mobile phone can take more than one SIM card, even of different types. The SIM and RUIM cards can be mixed together, and some phones also support three or four SIMs
[22][23]From 2010 onwards they became popular in India and Indonesia and other emerging markets,
[24] attributed to the desire to obtain the lowest on-net calling rate.
Display
Virtually all mobile phones have an integrated
display device, some with touchscreen function. The main measurements for
screen size varies greatly by model.
Manufacturers use different methods to specify display size, usually width and height in pixels or the diagonal measured in inches.
Central processing unit
Mobile phones have
central processing units (CPUs), similar to those in computers, but optimised to operate in low power environments.
Mobile CPU performance depends not only on the clock rate (generally given in multiples of
hertz)
[26] but also the
memory hierarchy also greatly affects overall performance. Because of these problems, the performance of mobile phone CPUs is often more appropriately given by scores derived from various standardized tests to measure the real effective performance in commonly used applications.
Mobile phones in society
Market share
Quantity Market Shares by Gartner
(New Sales) |
|---|
| BRAND | | | Percent | |
| Nokia 2009 | | 36.4% |
| Nokia 2010 | | 28.9% |
| Samsung 2009 | | 19.5% |
| Samsung 2010 | | 17.6% |
| LG Electronics 2009 | | 10.1% |
| LG Electronics 2010 | | 7.1% |
| Research In Motion 2009 | | 2.8% |
| Research In Motion 2010 | | 3.0% |
| Apple 2009 | | 2.1% |
| Apple 2010 | | 2.9% |
| Others-1 2009 | | 12.6% |
| Others-1 2010 | | 9.8% |
| Others-2 2009 | | 16.5% |
| Others-2 2010 | | 30.6% |
| Note: Others-1 consist of Sony Ericsson, Motorola, ZTE, HTC and Huawei.(2009-2010) |
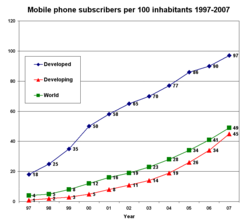
Mobile phone subscribers per 100 inhabitants 1997–2007

Global mobile phone subscribers per country from 1980-2009. The growth in users has been exponential since they were first made available.
The world's largest individual mobile operator by subscribers is
China Mobile with over 500 million mobile phone subscribers.
[27] Over 50 mobile operators have over 10 million subscribers each, and over 150 mobile operators have at least one million subscribers by the end of 2009 (source wireless intelligence). In February 2010, there were 4.6 billion mobile phone subscribers, a number that is estimated to grow.
[28]Competitive forces emerged in the Asia Pacific (excluding Japan) region at Q3 2010 to the detriment of market leader Nokia. Brands such as Micromax,
Nexian, and i-Mobile chipped away at Nokia's market share plus Android powered smartphones also gained momentum across the region at the cost of Nokia.
Based on IDC India, Nokia's market share dropped significantly to 36 percent in the second quarter, from 56.8 percent in the same quarter last year and further drop to 31.5 percent in the th ird quarter, reflecting the growing share of Chinese and Indian vendors of low-end mobile phones.
[29]Based on IDC in the last quarter of 2010, RIM has been knocked out from the top five list global mobile phone sellers. The number one rank is still Nokia followed by Samsung, LG Electronics, ZTE and Apple. For the first time Chinese ZTE is among the top five list and mainly make of lower cost phones.
[30]For the year of 2010, Sony Ericsson and Motorola are out from the top of five list and have been replaced by LG Electronics and Apple. Significant increase from 16.5 percent to 30.6 percent has been done by many small not yet recognized brands (some of them are new brands) – Others-2. Total sales in 2010 to end users were 1.6 billion units or increase by 31.8 percent from the year of 2009.
[31]In Q1 2011, Apple surpassed Nokia as the world's top handset vendor in revenue and Nokia market share drop continuously to 29 percent in Q1 2011 as the lowest level since the late 1990s. In June 2011, Nokia has also announced that in Q2 2011 the sales and margins are expected to be much lower than anticipated due to global competition in both low-and-high end markets.
[32]At April 6, 2011 market capitalization of HTC surpassed Nokia with $33.8 billion over $33.4 billion respectively. The credit agency was also downgraded Nokia's debt from A2 to A3.
[33]Market share of world's top 5 mobile vendor
- Source: Gartner & IDC, Q2-2011
- Note: Vendor shipments are branded shipments and exclude OEM sales for all vendors
By year-over-year at Q2, worldwide sales of mobile devices grew 16.5 percent, to reach 428.7 million units. Others still rose and achieved almost a half of market share.
June 2011: In 3 years, RIM has lossed about 82 percent of the capitalization. As a barometer in North America RIM's market share dropped significantly from 54 percent to 13 percent in the last 2 years.
[36]Other manufacturers outside of Top Five include (June 2011 data)
Research In Motion Ltd. (RIM),
HTC Corporation,
Motorola,
Huawei,
Sony Ericsson, while the following has very small market share each
Audiovox (now
UTStarcom),
BenQ-Siemens,
CECT,
Fujitsu,
Kyocera,
Mitsubishi Electric,
NEC,
Panasonic,
Palm,
Pantech Wireless Inc.,
Philips,
Qualcomm Inc.,
Sagem,
Sanyo,
Sharp,
Sierra Wireless,
Just5,
SK Teletech,
T&A Alcatel,
Trium,
Toshiba,
Vidalco and so many
China's,
India's and
Indonesia's brands. There are also specialist communication systems related to (but distinct from) mobile phones.
Media
In 1998, one of the first examples of selling media content through the mobile phone was the sale of
ringtones by Radiolinja in Finland. Soon afterwards, other media content appeared such as news, videogames, jokes, horoscopes, TV content and advertising. Most early content for mobile tended to be copies of legacy media, such as the banner advertisement or the TV news highlight video clip. Recently, unique content for mobile has been emerging, from the ringing tones and ringback tones in music to "mobisodes," video content that has been produced exclusively for mobile phones.
In 2006, the total value of mobile-phone-paid media content exceeded Internet-paid media content and was worth 31 billion dollars (source Informa 2007). The value of music on phones was worth 9.3 billion dollars in 2007 and gaming was worth over 5 billion dollars in 2007.
[37]The advent of media on the mobile phone has also produced the opportunity to identify and track
Alpha Users or Hubs, the most influential members of any social community. AMF Ventures measured in 2007 the relative accuracy of three mass media, and found that audience measures on mobile were nine times more accurate than on the Internet and 90 times more accurate than on TV.
[original research?]The mobile phone is often called the Fourth Screen (if counting cinema, TV and PC screens as the first three) or Third Screen (counting only TV and PC screens).
[weasel words] It is also called the
Seventh of the Mass Media (with Print, Recordings, Cinema, Radio, TV and Internet the first six).
Privacy
The movements of a mobile phone user can be tracked by their service provider and, if desired, by law enforcement agencies and their government. Both the
SIM card and the handset can be tracked.
[38] China has proposed using this technology to track commuting patterns of Beijing city residents.
[39]Usage
Examples
Mobile phones are used for a variety of purposes, including keeping in touch with family members, conducting business, and having access to a telephone in the event of an emergency. Some people carry more than one cell phone for different purposes, such as for business and personal use. Multiple SIM cards may also be used to take advantage of the benefits of different calling plans—a particular plan might provide cheaper local calls, long-distance calls, international calls, or roaming. A study by
Motorola found that one in ten cell phone subscribers have a second phone that often is kept secret from other family members. These phones may be used to engage in activities including extramarital affairs or clandestine business dealings.
[40] The mobile phone has also been used in a variety of diverse contexts in society, for example:
- Organizations that aid victims of domestic violence may offer a cell phone to potential victims without the abuser's knowledge. These devices are often old phones that are donated and refurbished to meet the victim's emergency needs.[41]
- The advent of widespread text messaging has resulted in the cell phone novel; the first literary genre to emerge from the cellular age via text messaging to a website that collects the novels as a whole.[42] Paul Levinson, in Information on the Move (2004), says "...nowadays, a writer can write just about as easily, anywhere, as a reader can read" and they are "not only personal but portable."
- Mobile telephony also facilitates activism and public journalism being explored by Reuters and Yahoo![43] and small independent news companies such as Jasmine News in Sri Lanka.
- Mobile phones help lift poor out of poverty. The United Nations has reported that mobile phones—spreading faster than any other information technology—can improve the livelihood of the poorest people in developing countries. The economic benefits of mobile phones go well beyond access to information where a landline or Internet is not yet available in rural areas, mostly in Least Developed Countries. Mobile phones have spawned a wealth of micro-enterprises, offering work to people with little education and few resources, such as selling airtime on the streets and repairing or refurbishing handsets.[44]
- In Mali and some African countries, villagers sometimes had to go from village to village all day, covering up to 20 villages, to let friends and relatives know about a wedding, a birth or a death, but such travel is no longer necessary if the villages are within the coverage area of a mobile phone network. Like in many African countries, the coverage is better than that of landline networks, and most people own a mobile phone. However, small villages have no electricity, leaving mobile phone owners to have to recharge their phone batteries using a solar panel or motorcycle battery.[45]
- The TV industry has recently started using mobile phones to drive live TV viewing through mobile apps, advertising, social tv, and mobile TV.[46] 86% of Americans use their mobile phone while watching TV.
- In March 2011, a pilot project experimenting with branchless banking was launched by the International Finance Corporation, a member of the World Bank, and Bank Harapan Bali, a subsidiary ofBank Mandiri—the biggest bank in Indonesia and one of the cellular operators in Bali. Its aim is to increase the amount of bank customers. In Indonesia, only 60 million people have a bank account even though banks have existed for more than a hundred years, whereas 114 million people have become users of mobile phones in only two decades. Branchless banking has been successful in Kenya, South Africa and Philippines.[47]
Sharing
In some parts of the world, mobile phone sharing is common. It is prevalent in urban India, as families and groups of friends often share one or more mobiles among their members. There are obvious economic benefits, but often familial customs and traditional gender roles play a part.
[48] For example, in Burkina Faso, it is not uncommon for a village to have access to only one mobile phone. The phone is typically owned by a person who is not natively from the village, such as a teacher or missionary, but it is expected that other members of the village are allowed to use the cell phone to make necessary calls.
[49]Restrictions
While driving

Texting in stop-and-go traffic in New York City
Mobile phone use while driving is common but controversial. Being distracted while operating a motor vehicle has been shown to increase the risk of accident. Because of this, many jurisdictions prohibit the use of mobile phones while driving. Egypt, Israel, Japan, Portugal and Singapore ban both handheld and hands-free use of a mobile phone; others —including the UK, France, and many U.S. states—ban handheld phone use only, allowing hands-free use.
Due to the increasing complexity of mobile phones, they are often more like mobile computers in their available uses. This has introduced additional difficulties for law enforcement officials in distinguishing one usage from another as drivers use their devices. This is more apparent in those countries which ban both handheld and hands-free usage, rather those who have banned handheld use only, as officials cannot easily tell which function of the mobile phone is being used simply by looking at the driver. This can lead to drivers being stopped for using their device illegally on a phone call when, in fact, they were using the device for a legal purpose such as the phone's incorporated controls for car stereo or
satnav.
A recently published study has reviewed the incidence of mobile phone use while cycling and its effects on behaviour and safety.
[50]In schools
Some schools limit or restrict the use of mobile phones. Schools set restrictions on the use of mobile phones because of the use of cell phones for cheating on tests, harassment and bullying, causing threats to the schools security, distractions to the students, and facilitating gossip and other social activity in school. Many mobile phones are banned in school locker room facilities, public restrooms and swimming pools due to the built-in cameras that most phones now feature.
Privacy
Mobile phones have numerous privacy issues.
Governments, law enforcement and intelligence services use mobiles to perform surveillance in the UK and the US They possess technology to activate the microphones in cell phones remotely in order to listen to conversations that take place near to the person who holds the phone.
[51][52]Mobile phones are also commonly used to collect location data. While the phone is turned on, the geographical location of a mobile phone can be determined easily (whether it is being used or not), using a technique known
multilateration to calculate the differences in time for a signal to travel from the cell phone to each of several
cell towers near the owner of the phone.
[53][54]Health effects
On 31st May 2011, the
World Health Organization confirmed that mobile phone use may represent a long-term health risk
[55][56], classifying mobile phone radiation as a "carcinogenic hazard" and "possibly carcinogenic to humans" after a team of scientists reviewed peer-review studies on cell phone safety.
[57] One study of past cell phone use cited in the report showed a "40% increased risk for
gliomas (brain cancer) in the highest category of heavy users (reported average: 30 minutes per day over a 10‐year period)."
[58] This is a reversal from their prior position that cancer was unlikely to be caused by cellular phones or their base stations and that reviews had found no convincing evidence for other health effects.
[56][59] Certain countries, including France, have warned against the use of cell phones especially by minors due to health risk uncertainties.
[60]The effect mobile phone radiation has on human health is the subject of recent interest and study, as a result of the enormous increase in mobile phone usage throughout the world (as of June 2009, there were more than 4.3 billion users worldwide
[61]). Mobile phones use
electromagnetic radiation in the
microwave range, which some believe may be harmful to human health. A large body of research exists, both
epidemiological and experimental, in
non-human animals and in humans, of which the majority shows no definite causative relationship between exposure to mobile phones and harmful biological effects in humans. This is often paraphrased simply as the balance of evidence showing no harm to humans from mobile phones, although a significant number of individual studies do suggest such a relationship, or are inconclusive. Other
digital wireless systems, such as data communication networks, produce similar radiation.
At least some recent studies have found an association between cell phone use and certain kinds of brain and salivary gland tumors. Lennart Hardell and other authors of a 2009 meta-analysis of 11 studies from peer-reviewed journals concluded that cell phone usage for at least ten years “approximately doubles the risk of being diagnosed with a brain tumor on the same ('ipsilateral') side of the head as that preferred for cell phone use.”
[62]In addition, a mobile phone can spread
infectious diseases by its frequent contact with hands. One study came to the result that
pathogenic bacteria are present on approximately 40% of mobile phones belonging to patients in a hospital, and on approximately 20% of mobile phones belonging to hospital staff.
[63] There have been concerns that cell phone radiation may be negatively affecting
honeybees,
[64][65] but the results have been disputed.
[66][64]Future evolution: Broadband Fourth generation (4G)
The recently released 4th generation, also known as
Beyond 3G, aims to provide
broadband wireless access with nominal data rates of 100 Mbit/s to fast moving devices, and 1 Gbit/s to stationary devices defined by the
ITU-R[67] 4G systems may be based on the
3GPP LTE (
Long Term Evolution) cellular standard, offering peak bit rates of 326.4 Mbit/s. It may perhaps also be based on
WiMax or
Flash-OFDM wireless metropolitan area network technologies that promise
broadband wireless access with speeds that reaches 233 Mbit/s for mobile users. The radio interface in these systems is based on all-IP
packet switching,
MIMO diversity,
multi-carrier modulation schemes,
Dynamic Channel Assignment (DCA) and
channel-dependent scheduling. A 4G system should be a complete replacement for current network infrastructure and is expected to be able to provide a comprehensive and secure IP solution where voice, data, and streamed multimedia can be given to users on a "Anytime, Anywhere" basis, and at much higher data rates than previous generations.
Sprint in the US has claimed its WiMax network to be "4G network" which most cellular telecoms standardization experts dispute repeatedly around the world. Sprint's 4G is seen as a marketing gimmick as WiMax itself is part of the 3G air interface. The officially accepted, ITU ratified standards-based 4G networks are not expected to be commercially launched until 2011. In March 2011,
KT from South Korea announced that they has expanded its high-speed wireless broadband network by
4G WiBro cover 85 percent of the population. It is the largest broadband network covered in the world, followed by Japan and US with 70 percent and 36 percent respectively.
[68] At the beginning of 2011, some major mobile phone companies have released their 4G mobile phones such as from Motorola, HTC and Samsung.
[69]See also














































